Stepping on the scale and seeing a sudden jump of a few pounds can be alarming. However, don’t panic just yet—it’s likely water weight. Water weight refers to the temporary excess fluid stored in the body’s tissues, and it can fluctuate significantly throughout the day. In fact, it’s possible to gain up to 5 pounds of water weight in a single day. The good news? With a few simple lifestyle changes, you can shed this excess water fairly quickly. Let’s explore what causes water retention and how you can manage it effectively.
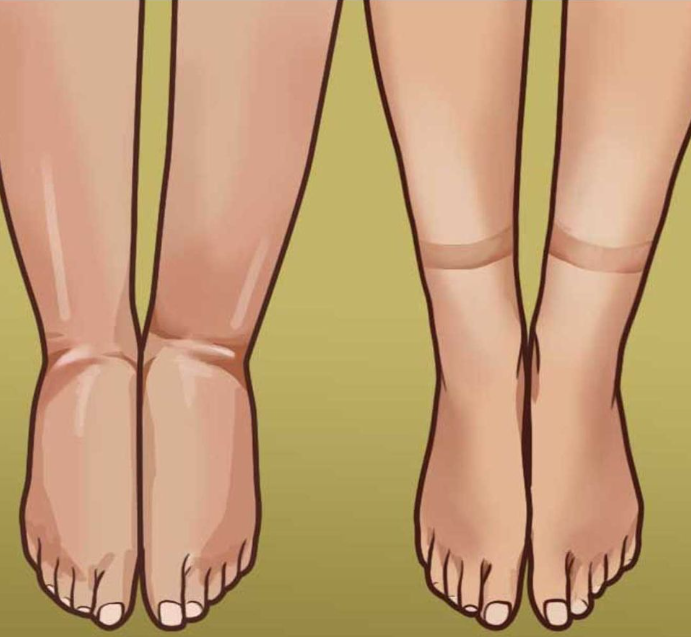
Causes of Water Retention
Water retention, also known as edema, can be caused by various factors, including diet, hormonal changes, physical activity, and even medical conditions. It occurs when the body holds onto extra fluid, which accumulates in the tissues and can cause swelling, bloating, and temporary weight gain. Understanding the root causes is essential to managing and preventing water weight.
Dietary Factors Contributing to Water Weight
What you eat plays a significant role in water retention. The amount of sodium, carbohydrates, and even water you consume can determine how much fluid your body retains. While some foods and habits contribute to water retention, others can help you flush it out. Let’s break down some of the most influential dietary factors.
How Sodium Affects Water Retention
Sodium is a major contributor to water retention. When you consume too much salt, your body holds onto extra water to dilute the excess sodium in your bloodstream. This can lead to bloating and puffiness, especially around the abdomen and face. Reducing your sodium intake can help your body release that excess water, making you feel lighter and less bloated.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Water Weight
Did you know that carbohydrates can cause your body to hold onto water? Carbs are stored as glycogen in your muscles and liver, and glycogen binds to water. For every gram of glycogen, your body retains about 3 grams of water. This means that high-carb meals can cause you to hold onto more water. Reducing your carb intake, especially refined carbs like bread and pastries, can help minimize water retention.
Hormonal Influences on Water Retention
Hormones play a crucial role in how much water your body holds onto. Estrogen, progesterone, and cortisol can all cause water retention, especially in women. Many women experience bloating and water weight gain around their menstrual cycle due to hormonal fluctuations. Similarly, stress increases cortisol levels, which can also lead to excess water retention.
Lifestyle Factors That Can Cause Water Weight Gain
Beyond diet and hormones, your daily habits also impact how much water weight you carry. Long periods of inactivity, such as sitting or standing still for too long, can cause fluids to pool in your legs and feet, leading to swelling. Lack of sleep, stress, and even a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to water retention. Making small adjustments to your lifestyle can help you shed that excess water and feel better overall.
How Exercise Can Impact Water Weight
Exercise can both increase and decrease water weight, depending on the intensity and type of workout. After an intense workout, your muscles may temporarily hold onto extra water as they repair and recover, which is completely normal. However, regular exercise improves circulation and promotes sweating, which helps the body release excess water and reduces bloating in the long run.
Effective Strategies for Reducing Water Weight
Now that we’ve covered the causes, let’s focus on solutions. The key to reducing water weight lies in simple dietary changes, hydration, and lifestyle adjustments. Here are some proven strategies to help you shed excess water:
The Importance of Hydration
It may sound counterintuitive, but drinking more water can actually help you lose water weight. When your body senses that it’s dehydrated, it holds onto water to prevent fluid loss. By drinking more water, you signal to your body that it’s well-hydrated, and it will begin to release the excess fluid. Aim for at least 8 cups of water a day to stay properly hydrated.
Tips for Reducing Dietary Sodium
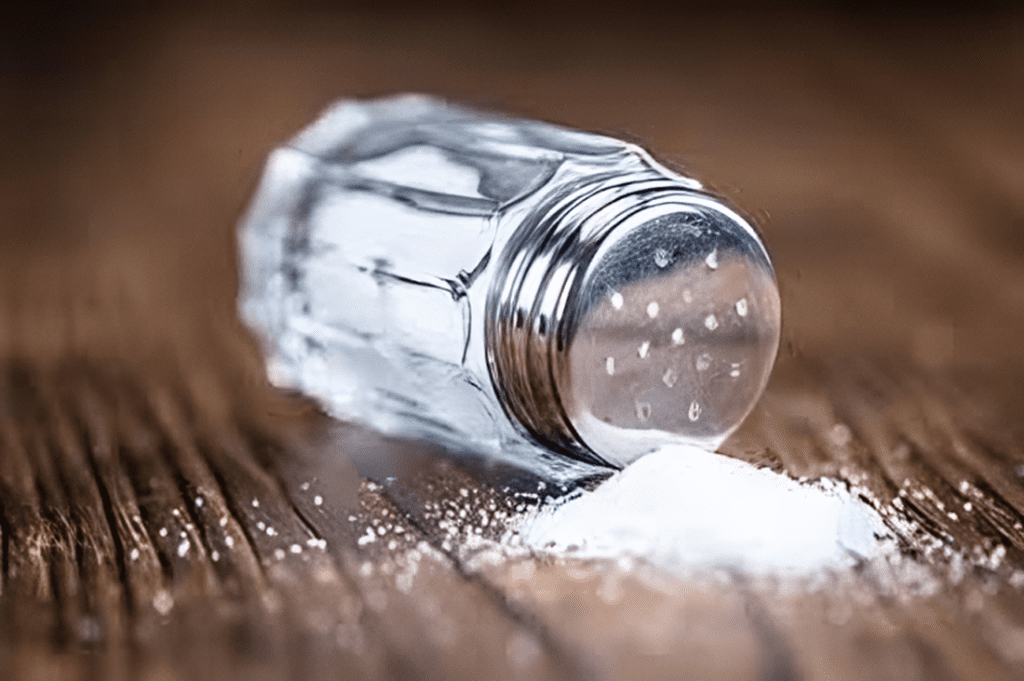

Cutting back on sodium is one of the most effective ways to reduce water retention. Start by avoiding processed and packaged foods, as these are often loaded with salt. Instead, opt for fresh, whole ingredients and season your meals with herbs and spices instead of salt. When shopping, always check the labels for sodium content to ensure you’re not consuming more than you should.
Incorporating Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body and promotes the elimination of excess fluid. Eating more potassium-rich foods such as bananas, spinach, avocados, and sweet potatoes can help you reduce water retention. Potassium works by signaling to your kidneys to excrete more sodium through urine, which helps flush out excess water.
Managing Carbohydrate Intake
To reduce water weight, consider moderating your intake of refined carbohydrates. Instead of loading up on white bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, focus on complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. These foods are slower to digest and cause less water retention compared to simple carbs.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Management
Beyond diet, certain lifestyle habits can make a huge difference in managing water weight. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to improve circulation and encourage your body to release water through sweat. Sleep is another important factor—getting enough rest helps your body regulate hormones and reduce cortisol levels, both of which can prevent water retention.
If you’re sitting or standing for long periods, try to take short breaks to move around. Elevating your legs can also help fluids return to your bloodstream and reduce swelling in the lower extremities.
When to Seek Medical Advice

While water retention is usually harmless, it can sometimes be a sign of an underlying medical condition such as kidney disease, heart failure, or hormonal imbalances. If you notice persistent swelling, especially in the legs or face, or if you experience unexplained water retention, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Your healthcare provider can assess the situation and offer targeted treatments if necessary.
Conclusion: Maintaining a Healthy Balance
Water weight can fluctuate dramatically, but with the right lifestyle changes, you can manage and shed excess fluid. Reducing sodium, moderating carbs, staying hydrated, and adopting a more active lifestyle are all effective strategies to maintain a balanced and healthy weight. Remember that some daily fluctuations are entirely normal, and the goal should always be long-term health rather than obsessing over short-term changes on the scale.
By understanding what causes water retention and how to address it, you can take control of your body and enjoy the benefits of feeling lighter, healthier, and more energized.


