Gray hair is often viewed as a natural sign of aging, yet some people experience it much earlier than expected. Seeing your first silver strands in your 20s or 30s can be surprising and even concerning. The reasons behind early graying vary, and it’s influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. If you’re wondering why some folks go gray earlier than others and what you can do to manage it, this article dives deep into the science and solutions behind premature graying.
The Science Behind Hair Color
Hair color is determined by melanin, the same pigment that colors your skin. Melanin is produced by melanocytes in your hair follicles. There are two types of melanin: eumelanin, which gives hair shades of black and brown, and pheomelanin, responsible for red and yellow hues. As we age, the activity of melanocytes gradually decreases, leading to less melanin production. Eventually, this results in gray or white hair.
However, aging isn’t the only factor. Various elements such as genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions can accelerate this process.
Genetics and Early Graying
The number one reason for premature graying is genetics. If your parents or grandparents went gray early, you are likely to follow in their footsteps. Recent research has identified specific genes linked to early graying, most notably the IRF4 gene, which regulates melanin production. Genetic predisposition plays a major role in determining when you will go gray, but it’s not the sole factor.
Even if you’re genetically inclined to gray early, other elements like diet and lifestyle can influence the speed at which it happens.
Environmental Factors: Sun, Pollution, and Chemicals
External environmental factors can also play a role in turning your hair gray faster than expected. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollution, and exposure to harsh chemicals all damage hair follicles and melanocytes. UV rays generate free radicals, which impair melanocyte function and reduce melanin production.
Similarly, using chemical treatments, like frequent hair dye or bleach, weakens your hair and its ability to maintain pigment. Protecting your hair from environmental stressors can help slow the graying process.
Lifestyle Influences: The Role of Smoking, Diet, and Sleep
Your lifestyle choices can significantly impact when and how quickly your hair turns gray. Here are some key contributors:
- Smoking: Research shows that smokers are more likely to experience early graying. The toxins in cigarettes cause oxidative stress, which damages melanocytes and accelerates aging.
- Diet: A poor diet lacking essential vitamins and minerals can deprive hair follicles of the nutrients they need to function optimally. Deficiencies in vitamin B12, copper, zinc, and iron can directly lead to hair thinning, weakening, and premature graying.
- Sleep and Stress: Lack of sleep and chronic stress are well-known accelerators of aging. Stress hormones, like cortisol, interfere with melanin production, while poor sleep hampers the body’s ability to repair and regenerate cells, including hair follicles.
Health Conditions and Nutritional Deficiencies

Certain health conditions can also contribute to early graying. Autoimmune diseases like vitiligo and alopecia areata can attack melanocytes, reducing melanin production and leading to white patches or premature gray hair.
Moreover, deficiencies in key nutrients, especially Vitamin B12, can lead to early graying. Vitamin B12 is essential for hair health, and a deficiency can damage hair follicles, leading to loss of pigment.
Ensuring that your diet is rich in the right vitamins and minerals is crucial for maintaining hair health and preventing premature graying.
Stress and Its Impact on Hair Color
We’ve all heard that stress can turn your hair gray, and while that’s partly true, it’s more complicated than it seems. Stress causes the body to produce higher levels of cortisol, which has been linked to the death of melanocytes in hair follicles. This is why those with chronic stress may notice their hair graying more quickly.
Additionally, stress causes oxidative stress, which accelerates the aging process, including the aging of hair follicles.
Preventive Measures and Treatments for Early Graying

While you can’t stop time or change your genes, you can adopt some habits to slow the process of graying. Here are several strategies:
Dietary Changes to Prevent Early Graying
One of the most effective ways to support hair health is through your diet. Focus on foods rich in vitamins and minerals that promote melanocyte function:
- Vitamin B12: Found in eggs, dairy products, and fish.
- Folic Acid: Leafy greens like spinach and kale are excellent sources.
- Copper and Zinc: Found in seeds, nuts, and whole grains.
- Iron: Found in red meat, legumes, and leafy vegetables.
By consuming a nutrient-rich diet, you can help nourish your hair from within and potentially delay graying.
Hair Care Products and Practices
Caring for your hair properly is essential in preventing premature graying and damage. Opt for gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners that are formulated with natural ingredients. These will help preserve your hair’s strength and avoid excessive drying or breakage.
Additionally, avoid frequent use of heat styling tools, as high heat can further weaken hair and cause it to lose its pigment more quickly.
Regularly massaging the scalp can also stimulate blood flow to the hair follicles, encouraging healthy growth and helping to maintain your hair’s natural color for longer.
Medical Treatments and Interventions
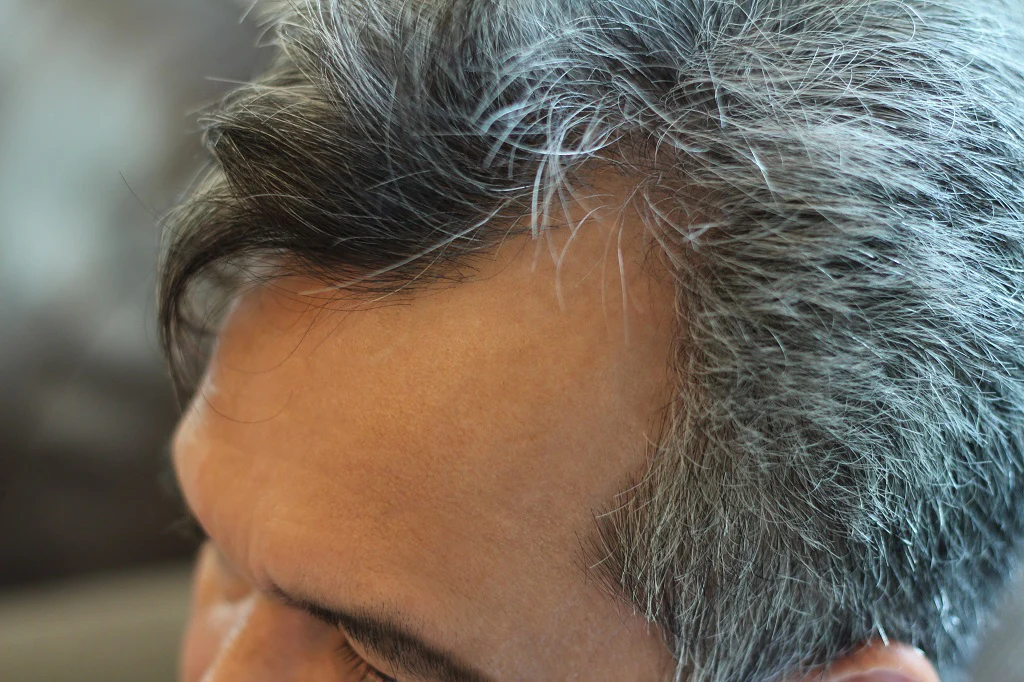

For those looking for medical solutions, some options may help slow or manage early graying:
- Topical treatments: Certain topical treatments containing catalase (an enzyme that helps break down hydrogen peroxide in hair follicles) may help reduce the oxidative stress that contributes to graying.
- Supplements: If a nutritional deficiency is causing your graying, taking supplements for Vitamin B12, folic acid, or other missing nutrients can help restore hair pigment.
- Cosmetic solutions: For those who prefer to cover their gray, hair dyes and colorants offer an effective way to conceal gray strands.
Conclusion: Managing Premature Gray Hair
Premature graying can be distressing, but understanding its causes—from genetics and lifestyle choices to environmental factors—can help you take control of the situation. While there’s no way to reverse graying completely, adopting a healthy lifestyle, protecting your hair from damage, and incorporating the right nutrients into your diet can delay the process.
Whether you choose to embrace your gray strands or explore treatments to manage them, the most important thing is focusing on overall health and well-being. After all, graying is just one small part of the complex and beautiful process of aging.


