Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by microscopic mites that burrow under the skin, leading to severe itching and a rash. It’s not just a problem in under-resourced tropical regions; it can affect people of all ages, backgrounds, and economic statuses. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of scabies, its symptoms, treatments, and ways to prevent its spread. Let’s dive in to understand how you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this irritating condition.
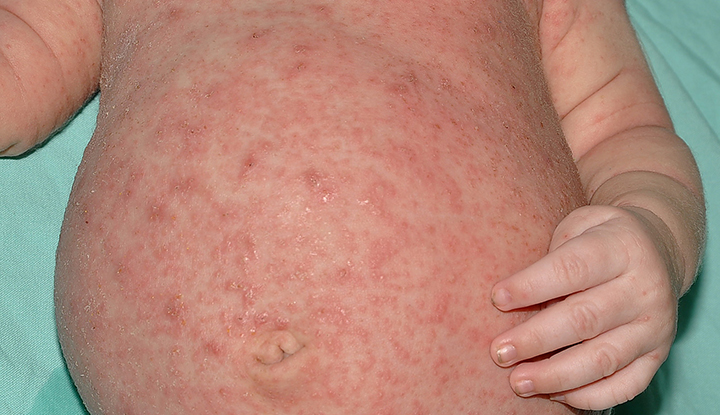
What is Scabies? An Overview of the Skin Condition
Scabies is an infestation of the skin caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These mites are tiny, white, eight-legged creatures that burrow under the skin to feed, live, and lay eggs. As the mites burrow, they trigger an allergic reaction, resulting in an extremely itchy rash that spreads over time. This skin condition spreads easily through close personal contact, making it a common issue in crowded environments like nursing homes, schools, dormitories, and prisons.
Unlike some skin conditions, scabies isn’t related to poor hygiene. It can affect anyone, regardless of how clean or careful they are. The key to managing scabies effectively lies in understanding its symptoms, transmission, and treatment options.
Types of Scabies: Classic, Crusted, and Nodular
Scabies generally presents itself in three forms:
Classic Scabies: This is the most common form and is characterized by intense itching and a bumpy rash. You may notice burrow-like tracks on the skin, indicating the presence of mites.
Crusted (Norwegian) Scabies: This severe form often affects individuals with weakened immune systems. It involves a thick crust of skin that harbors thousands to millions of mites, as opposed to the typical 10-15 mites found in classic scabies. It’s highly contagious and requires prompt medical attention.
Nodular Scabies: This variant is more common in children and affects areas like the genitals, armpits, and groin. It results in raised, itchy nodules that may persist even after treatment.
Symptoms of Scabies: Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
The main symptom of scabies is relentless itching, which often worsens at night. This itching results from an allergic reaction to the mites and their waste products under the skin. Other key symptoms include:
- Red, itchy rash: The rash may take 4-6 weeks to appear if it’s your first time experiencing scabies. It spreads gradually and can appear as hives, insect bites, or pimple-like bumps.
- Burrowing tracks: Look for thin, raised, skin-colored lines that may be visible on the surface of the skin.
- Sores and blisters: Persistent scratching can lead to sores or blisters, which increase the risk of secondary infections.
How Scabies Spreads: Understanding Transmission
Scabies spreads primarily through prolonged skin-to-skin contact, which is why it’s prevalent among people who share living quarters. It can also spread through:
- Sharing personal items: While less common, scabies mites can be transmitted through shared bedding, clothing, or towels.
- Crowded environments: Places like nursing homes, dorms, and shelters are high-risk areas for scabies outbreaks due to the close proximity of people.
However, you cannot get scabies from pets, as the mites that infest animals cannot survive on human skin.
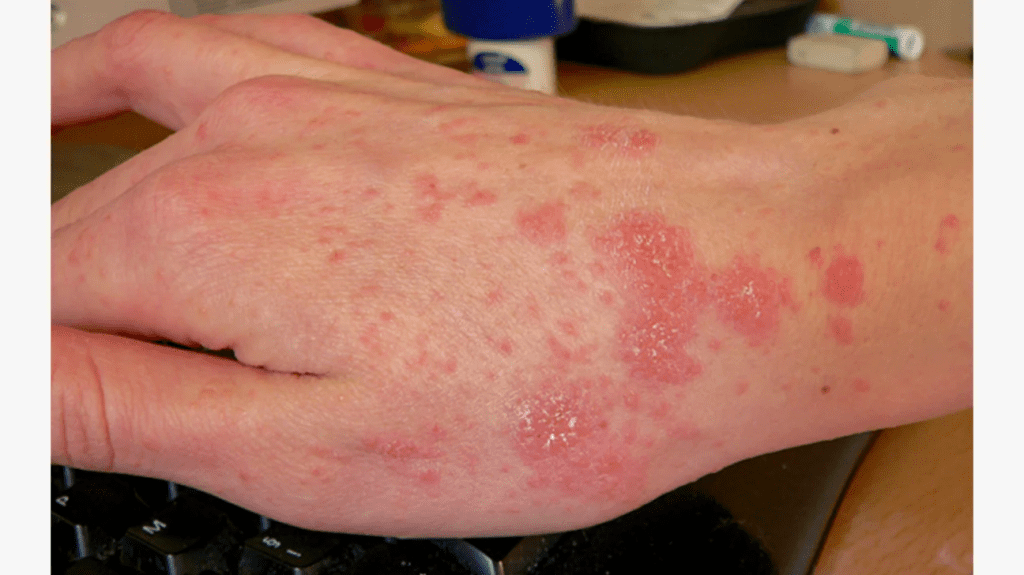
Diagnosing Scabies: How to Identify the Infestation
If you suspect scabies, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. The provider may examine your skin and even perform a skin scraping to confirm the presence of mites or eggs under a microscope. Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent further spreading.
Treatment for Scabies: How to Get Rid of Mites Effectively
Scabies requires medical treatment to eliminate mites completely. Here’s how it’s treated:
Topical Treatments: The most common way to treat scabies is through medicated creams, ointments, or lotions that are applied directly to the skin. Popular options include:
- Permethrin Cream: This is the most prescribed treatment for scabies. You should apply it to the entire body from the neck down and leave it on for 8-14 hours before washing it off.
- Crotamiton Cream or Lotion: This medication can be used as an alternative to permethrin.
- Sulfur Ointment: This is a safe treatment option for pregnant women and children.
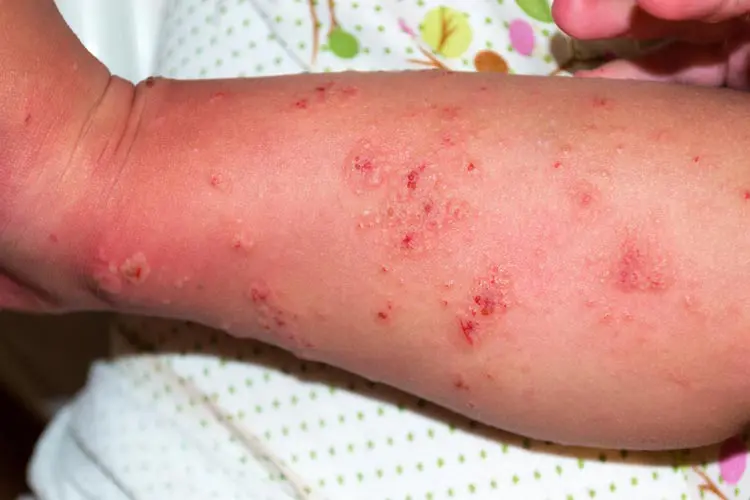
It’s essential to follow the application instructions closely, as treatment failure is often due to incorrect usage.
Oral Medications: If topical treatments are ineffective, your doctor may prescribe oral medications like ivermectin, which is an antiparasitic drug given in two doses. However, it’s not recommended for children under 15 kg (35 lbs), pregnant women, or nursing mothers.
Symptom Relief: Other medications like antihistamines (to reduce itching), antibiotics (to treat secondary infections), and steroid creams (to reduce inflammation) may also be prescribed.
How to Prevent Scabies: Essential Tips for Stopping the Spread
Prevention is key when it comes to scabies, especially in high-risk environments. Here’s how you can prevent scabies and stop its spread:
- Treat close contacts: Family members and sexual partners of infected individuals should receive treatment simultaneously, even if they don’t show symptoms.
- Wash linens and clothes: Wash bed linens, towels, and clothes in hot water and dry them on high heat to kill any mites.
- Seal unwashable items: Place items that cannot be washed, like stuffed toys or pillows, in sealed plastic bags for at least seven days. This duration ensures that mites die without a human host.
Avoid close contact with anyone diagnosed with scabies until treatment is complete.
What’s the Prognosis for Scabies?
Scabies can be highly uncomfortable, but it’s treatable. With proper medication, most people see significant improvement within a month, although itching may persist for up to two weeks after treatment. It’s critical to follow up with a healthcare provider if symptoms don’t improve or if new rashes develop.
Scabies won’t resolve on its own, so neglecting treatment can lead to chronic itching, skin infections, and the risk of spreading the condition to others.
Conclusion: Don’t Let Scabies Ruin Your Skin and Comfort
Scabies may be frustrating, but it’s manageable with the right treatment and prevention strategies. Early diagnosis, proper medication, and thorough cleaning of personal items are essential for effective recovery. If you suspect you have scabies, consult a healthcare provider, treat close contacts, and maintain good hygiene practices to prevent further outbreaks. Scabies can be a persistent itch, but you have the tools to get rid of it for good.


