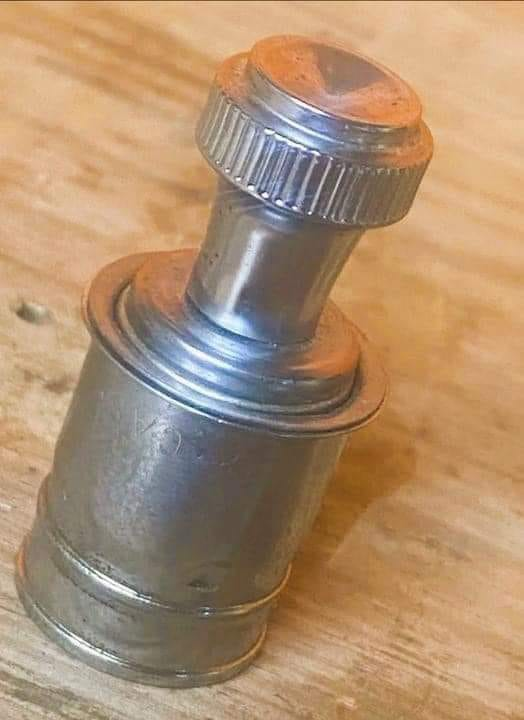
The cigarette lighter receptacle—also known as a cigar lighter socket—is a standard feature in most vehicles, serving as more than just a tool for lighting cigarettes. Initially intended to heat cigarette lighters, this outlet has become a versatile DC power source for various portable devices. While the design is convenient, it comes with specific limitations and potential hazards. This article will dive into the history, modern applications, and design considerations of cigarette lighter receptacles.

History of the Cigarette Lighter Receptacle
The origins of the cigarette lighter socket trace back to the early 1880s when German inventor Friedrich Wilhelm Schindler developed the first electrical cigar lighter, also known as “Cigarrenanzünder.” It was initially designed for lighting cigars, hence its original name. By the 1920s, as cigarettes gained popularity, it was renamed “cigarette lighter.”
Evolution in the Automotive Industry
- 1921: The first “cordless” cigarette lighter was patented in the U.S., featuring a removable heating element.
- 1925-1926: Cigarette lighters started to become standard equipment in cars, allowing drivers to light cigarettes conveniently.
- 1956: The modern “automatic” removable V-Coil lighter was developed by Casco, marking a significant innovation in the design of automotive lighters.
The traditional receptacle has since evolved into a universal power source for vehicles, capable of powering various electronics, from mobile phones to tire inflators.
The Dual Functionality: Lighting and Power Source
While the original purpose of the receptacle was to heat cigarette lighters, it has transformed into a general DC power outlet in modern vehicles. Despite this adaptation, the basic design remains largely unchanged, creating some challenges and limitations.
Use as a Cigarette Lighter
The traditional cigarette lighter is a metal cylinder containing a nichrome coil, which heats up when a high current (~10 amperes) is passed through it. Here’s how it works:
- The user pushes the lighter into the socket, pressing a bi-metallic strip that holds it in place.
- As the coil heats up, the bi-metallic strip bends, releasing the lighter after it becomes hot enough to ignite a cigarette.
- The user must then promptly remove the lighter to use it safely, as the device becomes extremely hot.
This classic mechanism has largely been phased out, with newer cars often replacing it with plastic covers labeled “12 V DC outlet.”
Use as a 12V Power Outlet
The modern cigarette lighter receptacle is primarily used to supply 12-volt DC power to various electronic devices, including:
- Mobile phone chargers
- GPS devices
- Portable coolers and warmers
- Small air compressors
Despite its convenience, the receptacle is far from perfect as a DC connector, primarily because it was not designed for frequent plug-ins or varying loads.
Design and Technical Specifications
Cigarette lighter receptacles have specific design features that allow them to function both as a lighter socket and as a general power outlet. Here’s a closer look at the specifications and components.
Plug and Socket Dimensions
There are two main types of 12-volt receptacles found in vehicles:
- Size A: Common in American cars, with a socket diameter of 20.93–21.01 mm and a plug diameter of 20.73–20.88 mm.
- Size B: More prevalent in European cars, with a socket diameter of 21.41–21.51 mm and a plug diameter of 21.13–21.33 mm.
The plug’s center point carries the positive voltage, while the outer casing serves as the negative (ground) connection.
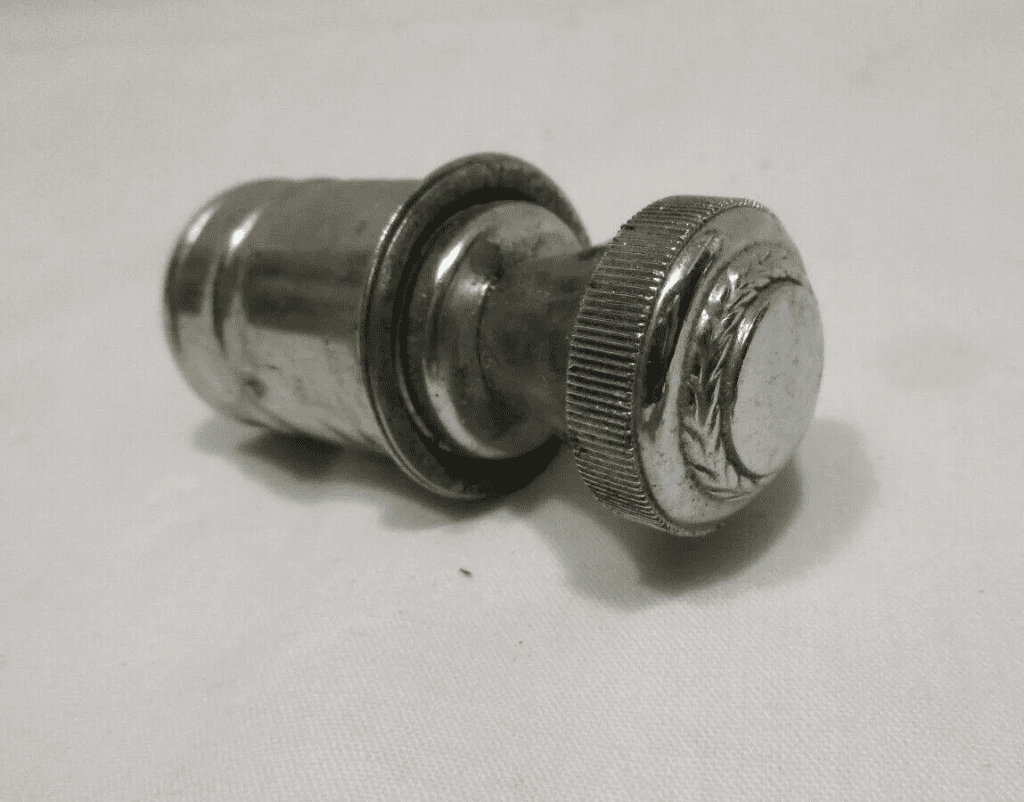

Power Ratings and Limitations
- Nominal Voltage: The receptacle supplies 12 volts DC, but the actual voltage can vary depending on the vehicle’s alternator and battery status. It can range from 12.5 volts when dormant to up to 14.5 volts when the engine is running.
- Current Limit: Most receptacles can handle a maximum of 10-15 amps, making them suitable for a wide range of low-power devices but unsuitable for high-power applications.
- Voltage Fluctuations: During vehicle operation, voltage can fluctuate significantly, especially during engine start-up or when the battery is low. Devices connected to the outlet should be able to tolerate these fluctuations to function reliably.
Advantages and Limitations as a Power Source
The cigarette lighter receptacle has become a de facto standard for providing DC power in vehicles. Despite its widespread use, it has certain limitations that users need to be aware of.
Advantages
- Wide Availability: Almost every car, truck, and recreational vehicle (RV) has at least one 12V socket, making it a convenient and universal power source.
- Versatility: It can power various devices, from phone chargers to GPS units, making it ideal for road trips.
- Backwards Compatibility: Even newer vehicles often retain the receptacle alongside USB ports, maintaining compatibility with older devices.
Limitations
- Low Reliability: The connection can be prone to vibration-induced disconnection, making it less reliable compared to other DC connectors like the Anderson Powerpole.
- Heat Generation: Poor contact can lead to heat buildup, potentially causing damage to the plug or receptacle.
- Voltage Irregularities: Voltage fluctuations can pose a risk to connected devices, particularly those that are sensitive to changes in power supply.
Alternative Power Options in Vehicles
As the automotive industry progresses, manufacturers are introducing more reliable and versatile power outlets, such as USB ports and dedicated DC connectors. These new outlets provide more stable power and are better suited for modern electronic devices.
1. USB Ports
USB ports offer a more reliable and stable source of power for smaller electronic devices. They typically supply 5 volts DC and are less prone to disconnection issues, making them ideal for charging smartphones and tablets.
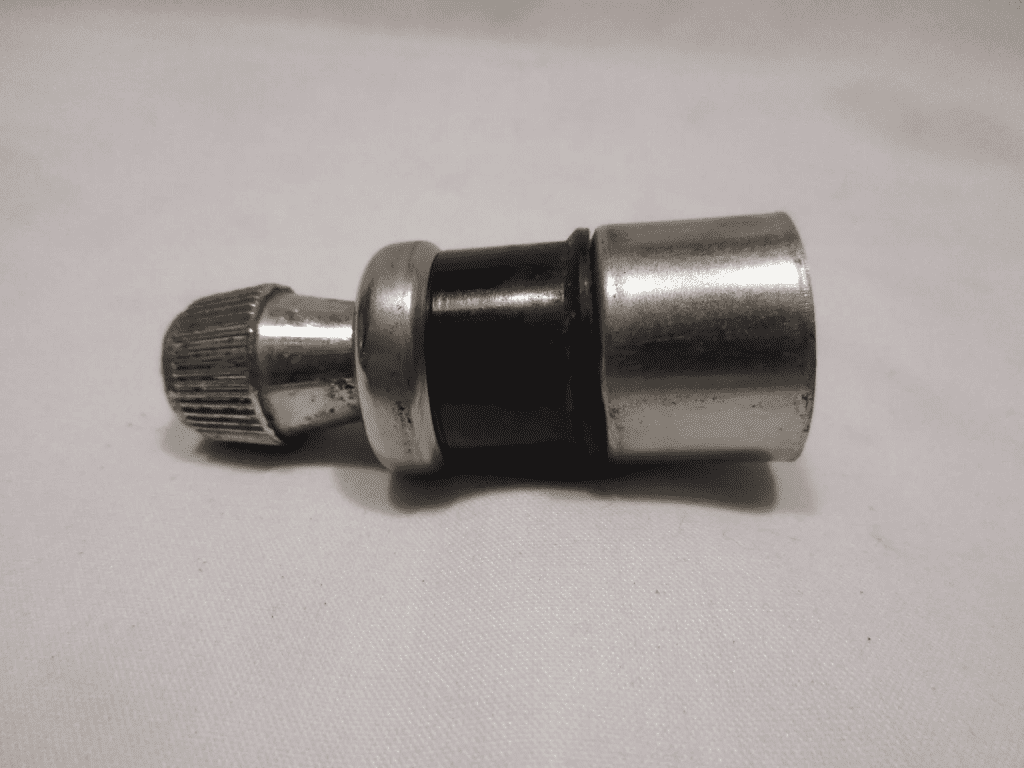

2. Anderson Powerpole Connectors
These connectors are often used in amateur radio and emergency response vehicles due to their secure fit and higher current capacity. They offer a more reliable connection than the standard cigarette lighter socket and are less likely to vibrate loose.
3. Inverter Outlets
For devices that require AC power, vehicles can be equipped with inverter outlets. These inverters convert 12V DC to 120V AC, allowing drivers to use standard household appliances like laptops, small TVs, or mini-fridges.
Conclusion: The Future of 12V Power in Vehicles
The cigarette lighter receptacle has played a crucial role in providing power to various devices in vehicles, evolving from its original purpose of lighting cigarettes to becoming a universal 12V DC power source. While it offers versatility and wide compatibility, it falls short in terms of reliability and safety compared to newer connectors. As vehicles continue to integrate modern technologies, the cigarette lighter socket may eventually be replaced by more stable and efficient power outlets, making driving experiences safer and more convenient.