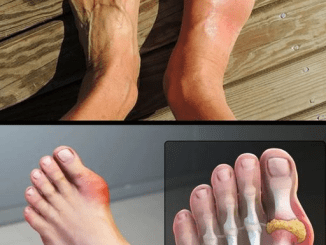
Blood clots are a potentially life-threatening condition that can escalate quickly if left untreated. While clotting is essential to prevent excessive bleeding, abnormal blood clots can block blood flow and lead to serious complications. Recognizing the early signs of a blood clot is critical for prompt action. In this article, we’ll break down seven common signs of a blood clot and explain what steps you should take next to protect your health.
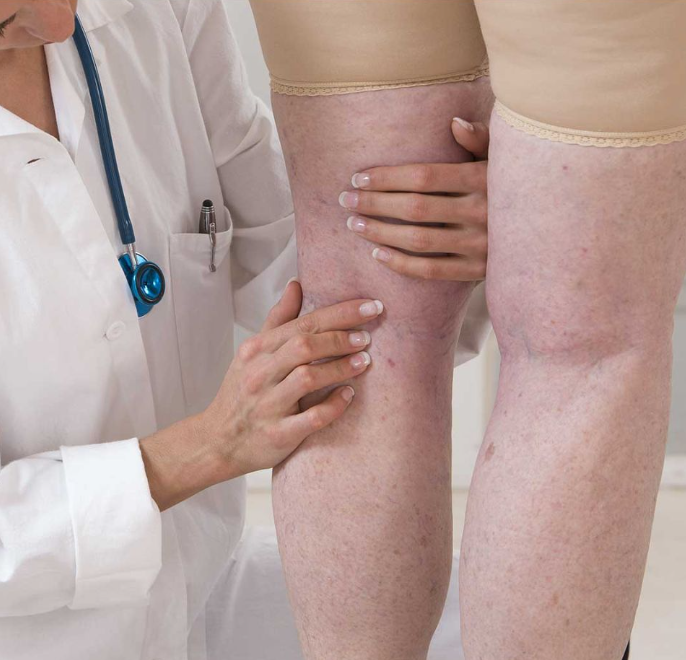
Understanding Blood Clots
Blood clots, also known as thrombi, are clumps of blood that change from liquid to semi-solid form, usually as a response to injury. However, when clots form inside veins or arteries without a clear injury, they can obstruct blood flow, leading to conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). These conditions can be life-threatening if not treated immediately. Understanding the warning signs can help you act quickly.
Sign 1: Swelling in the Affected Area
One of the most common signs of a blood clot is unexplained swelling, especially in the legs. The swelling usually occurs in one limb, typically the calf or thigh, and is caused by the clot blocking the flow of blood. This forces fluid to build up in the surrounding tissue, causing noticeable puffiness. The swelling may appear suddenly and can be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or heaviness in the affected limb.
If you notice significant swelling, especially if it’s localized to one leg, don’t ignore it. This could be an early sign of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Sign 2: Pain or Tenderness
Persistent pain or tenderness in the area of the clot is another key warning sign. Often mistaken for a muscle cramp or strain, this discomfort usually starts in the leg, particularly in the calf. The pain can be sharp, throbbing, or dull and tends to worsen over time, especially when you walk or move the affected limb. If the pain persists and doesn’t seem to improve, it’s important to consider that it might be more than just a muscle issue.
This pain occurs because the clot is blocking normal blood flow, causing inflammation and irritation in the vein. Seek medical evaluation if the pain escalates or if it’s accompanied by other symptoms.
Sign 3: Red or Discolored Skin
A blood clot can cause noticeable changes to the skin above the affected area. If you see that the skin has turned red, bluish, or purplish, it’s a signal that blood flow is restricted. In addition to the color change, the skin might appear stretched, shiny, or warmer than usual. This redness or discoloration happens because the clot is blocking blood from returning to the heart, causing blood to pool in the affected area.
If you notice these skin changes, don’t wait—this could be a strong indicator that a blood clot has formed, and you need medical attention.
Sign 4: Warmth in the Affected Area
Another common sign of a blood clot is warmth over the area where the clot has formed. This warmth is a result of inflammation caused by the clot blocking the vein. You might also feel tenderness when touching the area, making it more sensitive than usual.
If you detect any warmth combined with other symptoms like swelling, redness, or pain, it’s essential to take immediate action. A healthcare provider can perform tests to determine whether you have a clot.
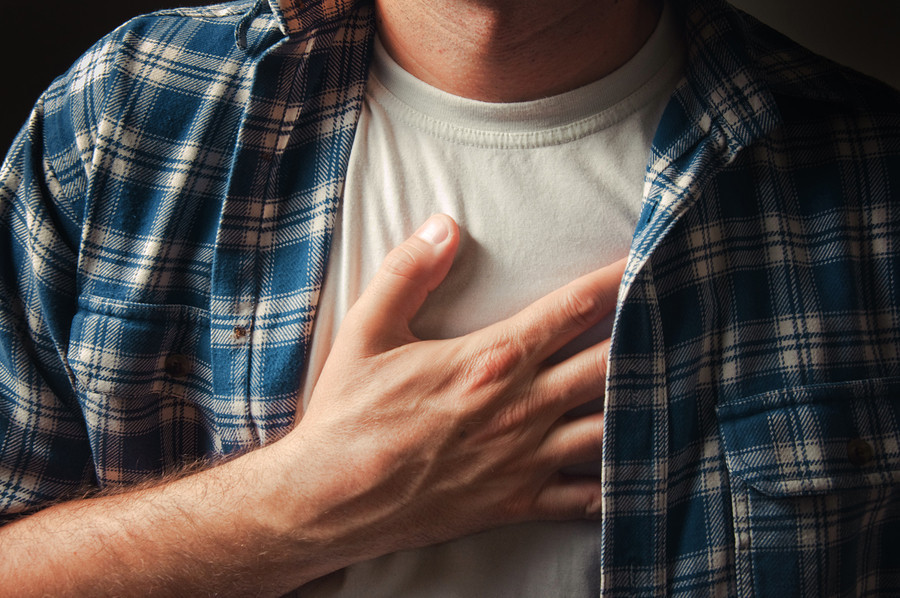

Sign 5: Sudden Shortness of Breath
When a blood clot moves to the lungs, it becomes a pulmonary embolism (PE), a life-threatening condition. One of the most alarming signs of a PE is sudden shortness of breath, which can happen without warning. This symptom may be accompanied by a rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or feeling faint. If you experience any difficulty breathing, especially in conjunction with other symptoms like leg pain or swelling, it is crucial to get emergency medical help immediately.
Sudden shortness of breath should never be ignored, as it indicates that the blood clot may have moved to the lungs, blocking oxygen flow and putting your life at risk.
Sign 6: Chest Pain or Discomfort
Chest pain or discomfort is another serious sign of a pulmonary embolism (PE). This type of pain can feel sharp or stabbing and often worsens when you take deep breaths or cough. The pain may mimic symptoms of a heart attack, which can make it confusing to identify at first. Regardless, chest pain of any kind is a red flag that demands immediate medical attention.
If you or someone you know experiences chest pain along with other symptoms like shortness of breath, do not wait—call for emergency medical help right away.

Sign 7: Rapid Pulse or Heart Rate
A rapid heart rate, also known as tachycardia, can be a sign that your cardiovascular system is working overtime due to a blood clot. The clot strains the heart as it struggles to circulate blood, resulting in a racing pulse. If you experience an unusually fast heart rate, especially when combined with symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, it’s critical to seek medical attention immediately.
Your body’s cardiovascular system can only compensate for so long when a blood clot is present, so don’t delay getting help if you notice this symptom.
What to Do If You Suspect a Blood Clot
If you recognize any of these signs, it’s vital to take them seriously. Do not massage the affected area—this could cause the clot to dislodge and travel to another part of your body, such as the lungs. The best course of action is to seek immediate medical attention. A doctor will likely use diagnostic tools like an ultrasound, CT scan, or blood tests to confirm the presence of a clot. Treatment typically involves anticoagulants, or blood thinners, which prevent the clot from growing or new clots from forming. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required.
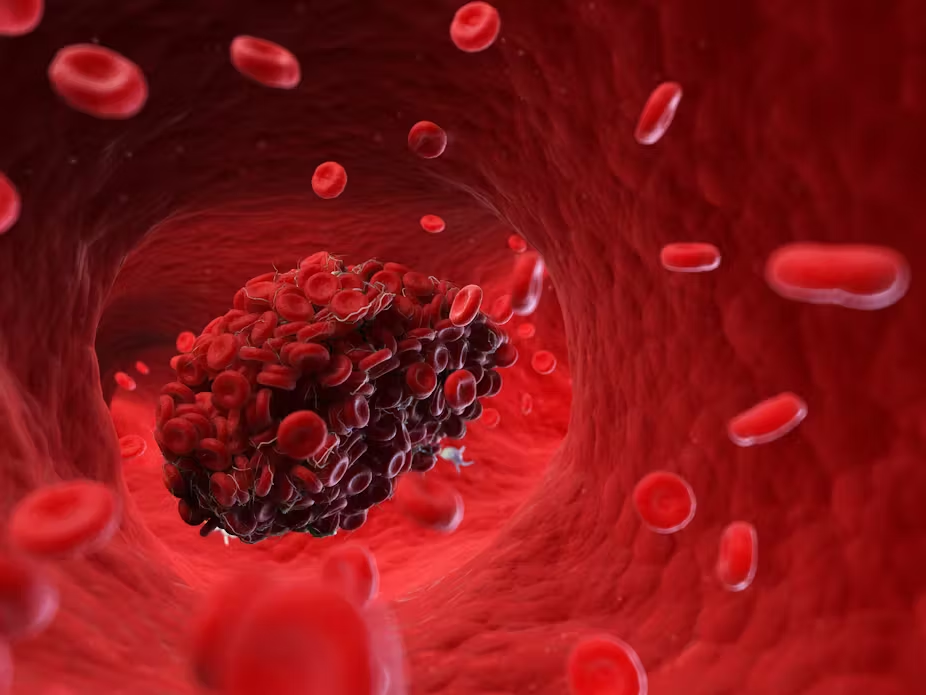
Prevention Measures
While blood clots are a serious health concern, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Staying active is one of the best ways to prevent clots, as movement keeps blood circulating properly. Avoid sitting or standing for long periods, especially on long flights or car trips. Staying hydrated and wearing compression stockings can also help. If you have any health conditions that put you at a higher risk, consult with your doctor about possible preventative medications, like blood thinners.
Conclusion
Blood clots are a medical emergency that require swift action. Recognizing the early signs—such as swelling, pain, or sudden shortness of breath—can save your life. If you suspect a clot, avoid self-treatment and seek medical help immediately. By staying aware and taking preventive measures, you can protect yourself from the dangerous consequences of blood clots.